The Mechanical Hive: a Lunar Habitation Project
"An innovative design that ensures resilience in the lunar environment while combining sustainability with lunar exploration" by Jonathan Kholi & Aarya Limbani
Introduction to Moon Habitation
A rocket departing from Earth bound for the moon is a feat of precision and ambition. It travels into the emptiness of space after escaping the gravity of Earth. Its engines fire with precise accuracy as it gets closer to the moon, gradually slowing it down. When the lunar surface is in view, the rocket uses powerful navigational systems to make a controlled descent. A historic feat in human space exploration and the start of a new era in lunar exploration are marked as the craft gently presses down, scattering particles and dust.

Site Selection
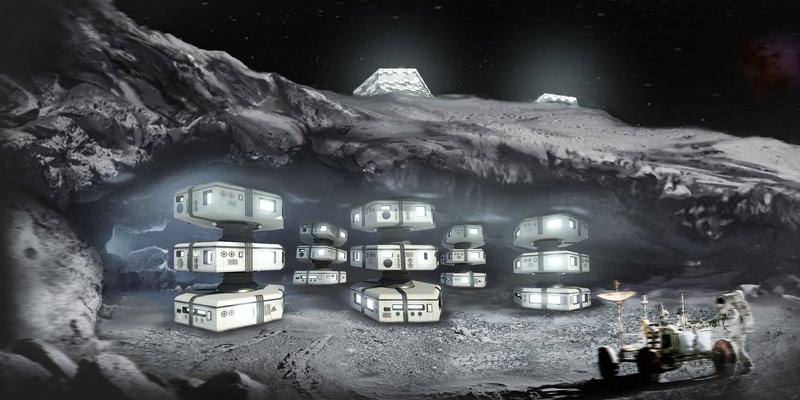
Selecting Malapert Mountain near the Shackleton crater at the lunar south pole as a site for lunar activities and scientific exploration indeed offers several advantages: -Continuous Solar Power: Malapert Mountain is exposed to the Sun most of the time due to its location near the Peak of Eternal Light. This provides an excellent opportunity for sustained power generation using solar panels. -Proximity to Shackleton Crater: Being just 116 kilometers (69.8 miles) away from Shackleton Crater is advantageous. It enables the provision of power and communications to the crater, potentially supporting future lunar activities there. Shackleton Crater is also valuable for astronomical observations, especially in the infrared spectrum, due to its extremely low temperatures. It could serve as a valuable location for space-based telescopes, shielded from Earth’s radio interference. -Resource Potential: The nearby Shoemaker and other craters, which are in constant deep shadow, may contain valuable concentrations of hydrogen and other volatiles. -Line of Sight Communications: Malapert Mountain’s elevation at around 5,000 meters (16,000 ft.) offers line-of-sight communications over a significant area of the Moon which is helpful for relaying data and signals to and from Earth.
Power Generation
The addition of solar panels to lunar habitats marks a significant step toward self-sufficiency and sustainability. These solar panels, specifically designed for the unique challenges of the lunar environment, capture the sun's energy to provide vital power for life support systems, lighting, and scientific equipment. By harnessing the abundant solar energy available on the moon's surface, lunar bases can reduce their dependence on Earth for energy supply, paving the way for extended human presence and lunar research while minimizing the environmental impact on our celestial neighbor.
Protection from Asteroids & Meteorites
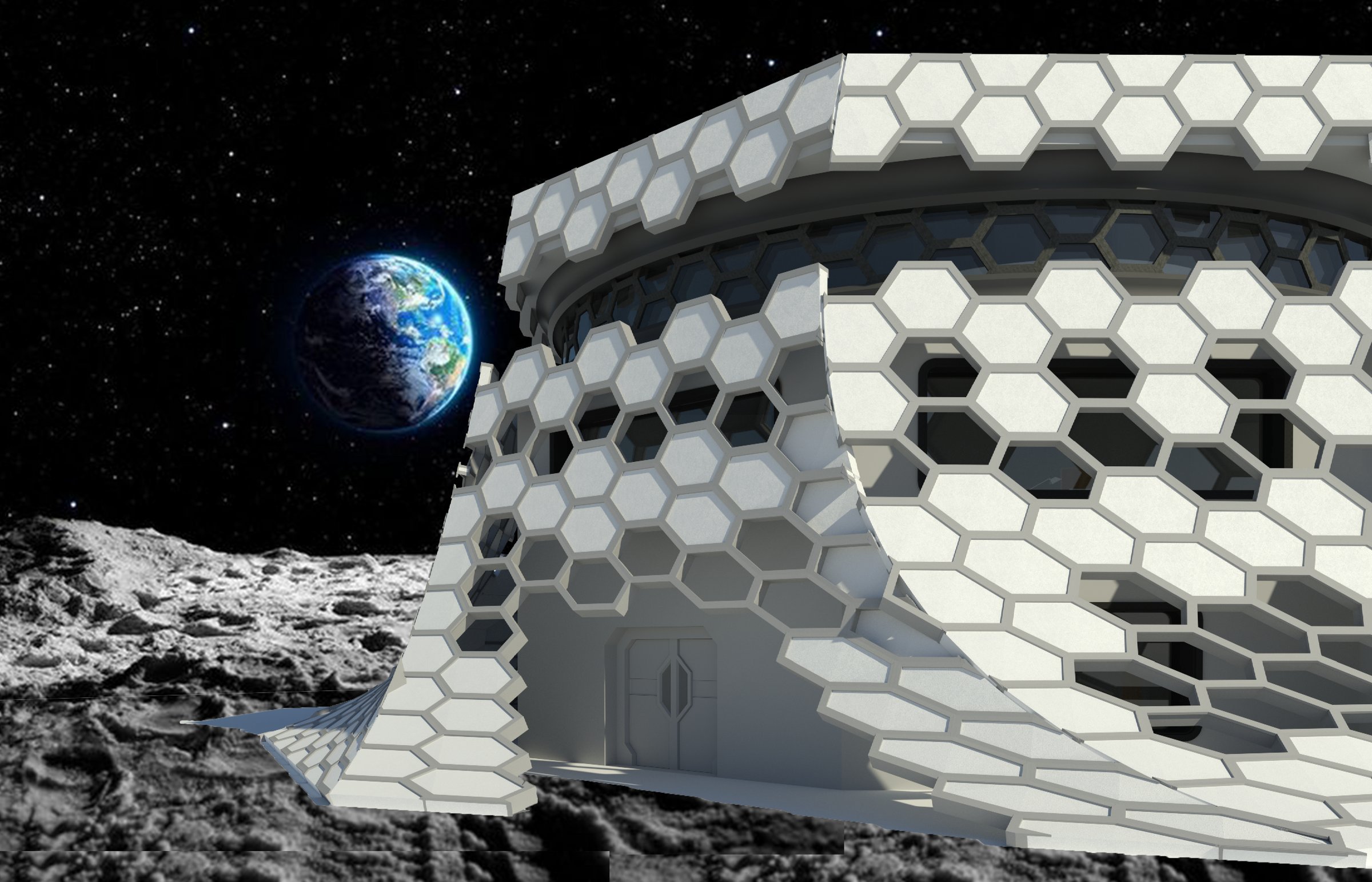
Hexagonal-shaped mesh structures offer a compelling solution for lunar habitats, providing both structural stability and protection against asteroid and meteorite impacts. Hexagons distribute loads evenly across their interconnected nodes, maximizing strength while minimizing material usage. This stability is vital for lunar structures, especially in the face of seismic activity. Additionally, the mesh acts as a protective outer layer, absorbing and dispersing the kinetic energy of incoming projectiles. This feature makes it an effective shield against smaller asteroids and meteorites, reducing the risk of damage to the lunar base and enhancing the safety of future lunar missions.
Observatory
A lunar habitat observatory offers an uncommon opportunity for astronomical observation and scientific research. It provides an excellent vantage position for examining the lunar landscape, Earth, and the universe because it is either on the moon's surface or within the habitat. By bridging the gap between lunar exploration and the secrets of the universe, this lunar observatory advances our knowledge of the cosmos and promotes a closer relationship between humanity and the cosmos.
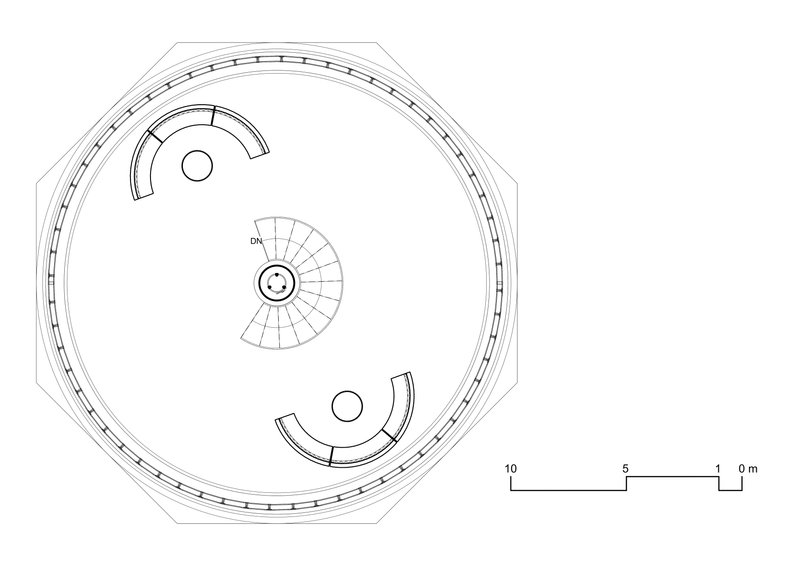
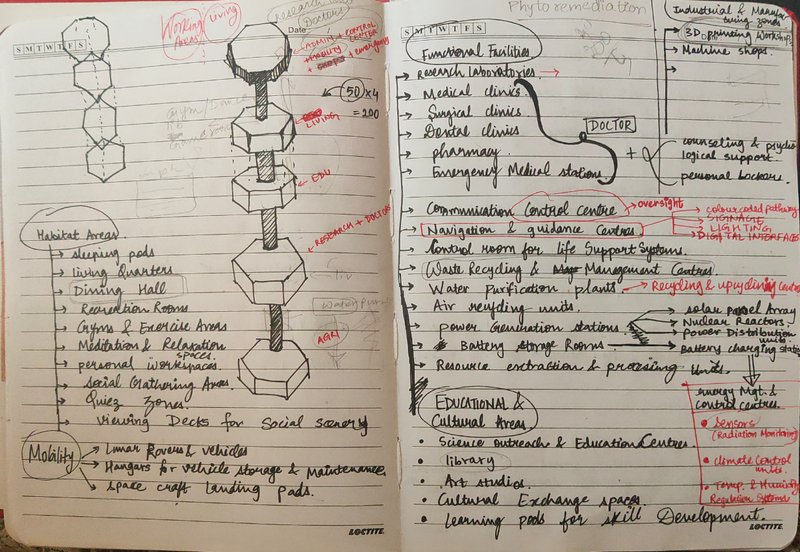
Administrative Blocks
The urban block, designed with meticulous consideration, is a testament to holistic living and sustainable practices. At its pinnacle, the administrative unit presides, serving as the nerve center of governance and community organization.
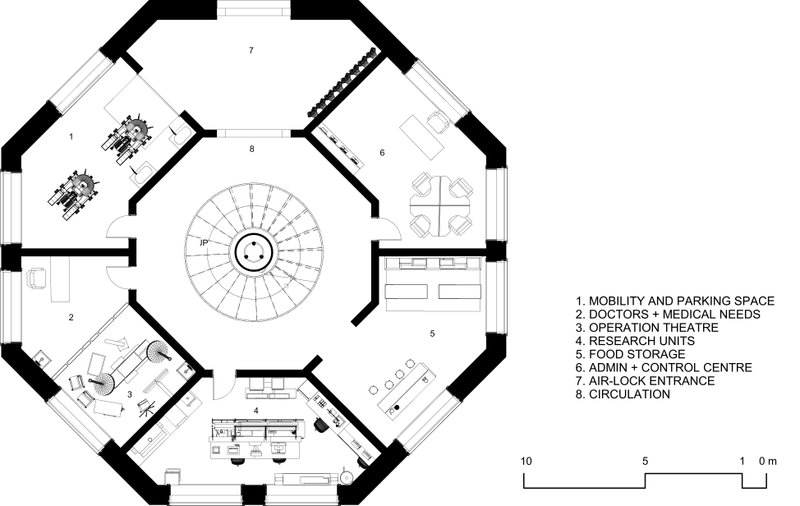
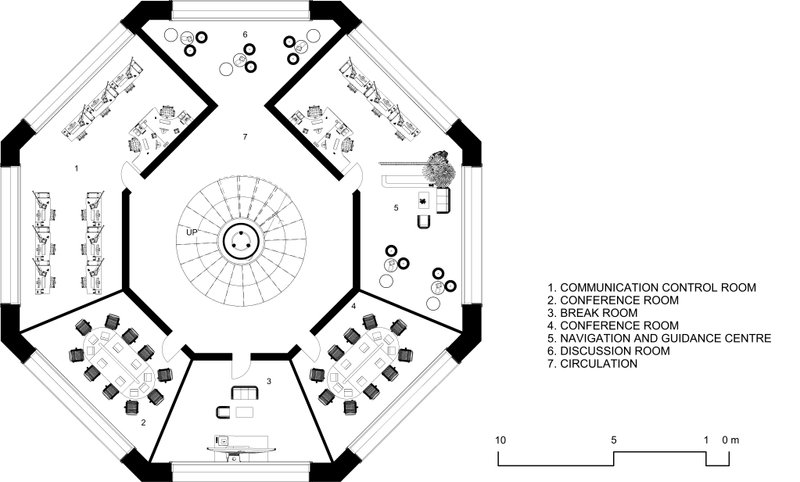
Living Units
Descending to the heart of the block, living cells on the second and third levels offer a comfortable and harmonious habitat, while interspersed recreational spaces foster community interaction and well-being. The architectural layout encourages social connections and enriches the quality of life for residents.
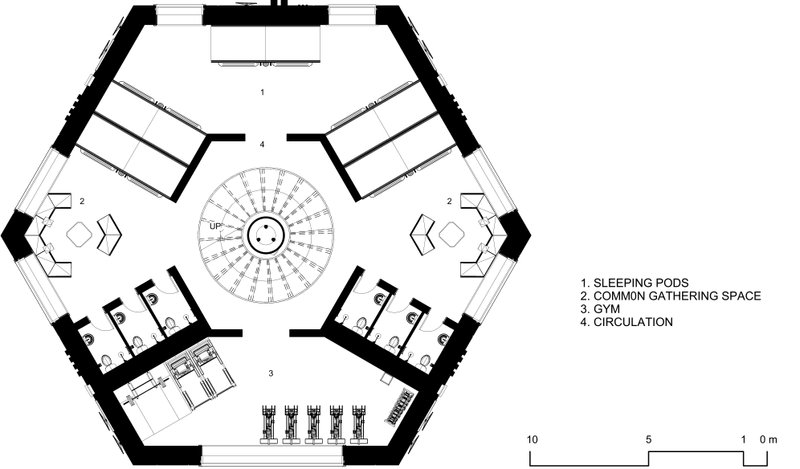
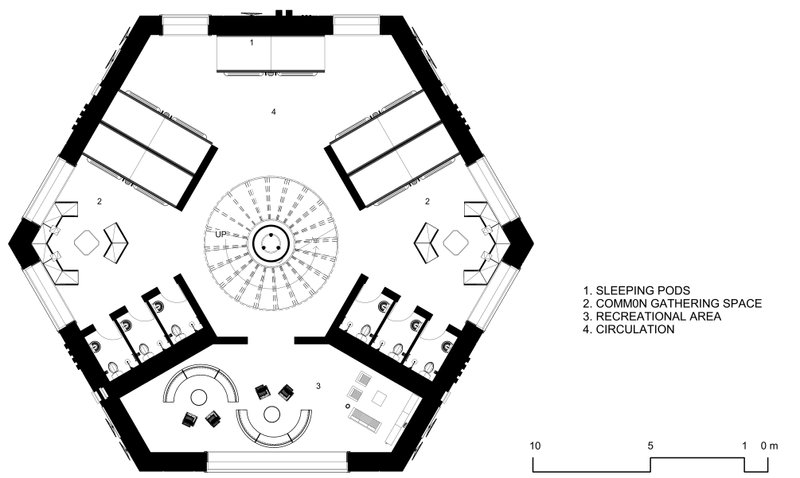
Agriculture, Research & Waste Management units
At the base, the final unit is dedicated to agricultural and research activities, symbolizing the fusion of urban living and environmental stewardship. Here, sustainable farming practices thrive alongside cutting-edge research facilities, cultivating innovation and self-sufficiency. Waste management completes the cycle, efficiently converting waste into valuable resources for agricultural use.
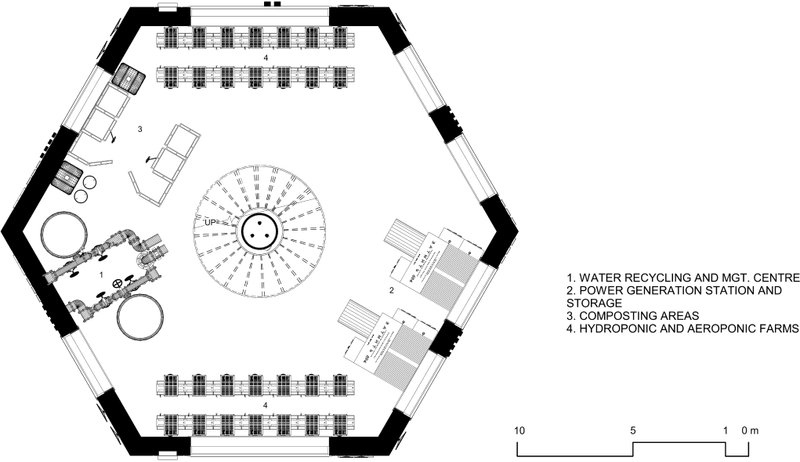
F.A.Q.
1. What was the concept behind the project?
The hexagonal shape stands as a fundamental concept to the ingenious design of a nut and bolt system. This geometric choice offers remarkable advantages in structural integrity and efficiency reducing the risk of deformation.
A hexagonal base, slightly rotated from its traditional orientation, offers increased structural strength and stability. This design modification disperses stresses more effectively across its surface, reducing the risk of deformation or collapse under load.
The six-sided symmetry of the nut form units ensures equal distribution of force, reducing the risk of deformation and enhancing the system’s durability.
A hexagonal mesh deployed in space presents a novel solution for preventing meteor impacts. Its geometric efficiency and strength make it a promising shield against incoming meteors, potentially safeguarding Earth from catastrophic collisions. This innovative concept underscores the power of geometry in planetary protection.
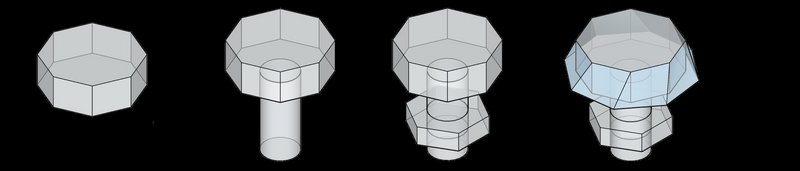
2. How many iterations were tried to arrive at the final outcome?
The project haven't deviated massively from the original idea, hence had 3 iterations .Initially, our project prioritized survival essentials for moon colonization, including life support systems, radiation shielding, and sustainable resource management. Then, a shift towards exploration and resource extraction became paramount. The design now incorporate advanced mining and extraction facilities to harness lunar resources like water ice and regolith for life support, fuel, and construction materials. These facilities, combined with innovative technologies, enable lunar colonies to become self-sustaining and reduce reliance on Earth for supplies. This strategic evolution in architectural focus not only ensures long-term survival but also paves the way for sustained lunar exploration and a gateway to deeper space exploration.
3. What/How were the materials chosen?
Using 3D printing to build a base on the moon is a fastest and a visionary concept that offers several key benefits:
- 3D printing can use lunar regolith (moon dust) as a raw material, reducing the need to transport heavy construction materials from Earth.
- 3D printers can manufacture and assemble parts quickly, allowing them to adapt to unforeseen challenges and build facilities efficiently.
- Building a base on the moon using 3D printing promotes sustainability by reducing waste and energy consumption during construction
4. How does the design generate and sustain power?
Energy generation on the Moon Base is primarily achieved through advanced solar panel arrays. These panels harness the abundant sunlight on the lunar surface, converting it into electricity to power essential systems, ensuring sustainability and self-sufficiency in the harsh lunar environment.
5. How are the life support systems conceived in the design?
A closed-loop waste management system efficiently recycles resources on the Moon Base. Hydroponic and aeroponic systems cultivate food, while CO2 recycling and algae contribute to survival. Excreta becomes valuable manure. The Moon Base employs an intricate water recycling cycle, reclaiming and purifying water from various sources. This sustainable approach ensures a consistent supply of clean water for hydroponics, hydration, and life support, underscoring the commitment to self-sufficiency and environmental stewardship.
6. How was the programme condensed into final?
The project aimed to harmoniously blends functionality with a futuristic aesthetic. Structures balance minimalism for efficiency with sleek, modern designs. This fusion of form and function not only ensures survival but also adds an element of wonder to lunar living.
7. What is the expansion plan of the project?
After establishing the mother base as a headquarter, the project can continue to add new units and modules to the lunar base to meet the needs of the growing population. These structures will include habitats, research facilities, education and training, international cooperation, and agricultural and energy production methods.